Rose production methods
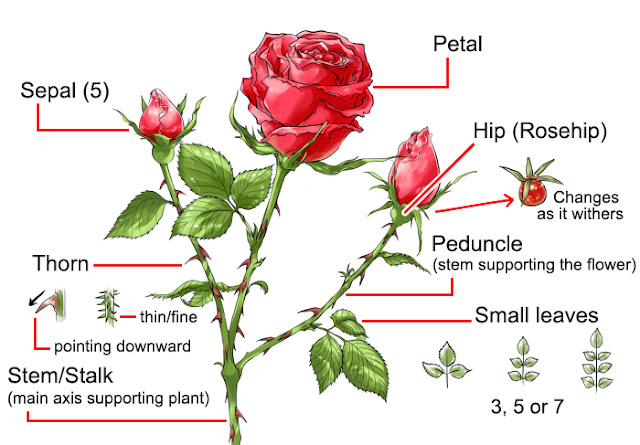
Rose plant structure
Students will be demonstrated about different plant parts.
Truss:
A group of flowers containing their own individual pedicleunited to one stem.
Suckers:
Suckers are off-shoots. In case of grafted roses, they develop from rootstock.
i)Any branch below the bud union is a sucker. Their removalis important at an
early stage, because they suppress the growth of main grafted/ budded plant and
may grow rapidly compared to grafted scioncultivar
ii)Any branch growing upright and appears different in foliage color, is usually
sucker which can be easily recognized.
Snag:
The small portion of branch left behind after pruning of rose canes, is called snag.
Stipule:
An outgrowth at base of petiole, is called stipule.
Cane:
Main stem/basal shoots of rose plant, is termed as cane.
Breaking Bud:
A bud which just start sprouting/growing, is called breakingbud.
Blind Shoot:
A shoot which grows vegetatively but do not produce flower.
Neck:
Area of a rose plant near ground surface level, is termed asneck
Prickles:
Sharp needle-like outgrowths/structures present on rose stems/canes, which have base
in epidermal layers, are called prickles. These are dead cells and can easily be detached from
parent branch. They are not true thorns because thorns havebase in wood and cannot be
separated. For e.g. in citrus.
Leaves:
Rose plants have compound leaves with 3, 5 or 7 leaflets.
Receptacle:
Basal part of rose flower which matures into a hip.
Hip:
Rose false fruit, usually of red, brown or black colour, which contain rose fruit and
rose seeds, is called rose hips. These are rich source of ascorbic acid (Vitamin C).
MAJOR PESTS OF ROSE
•Aphid:
Attack in March when the new growth starts.
These tiny insects are brown or green colored and make colonies just below buds and
Control: Initially by spraying water with pressure. At later stages, by spraying
insecticides, e.g., Polo, Confidor.
•Thrips:
The worst problem of roses in Pakistan. Small brownish insects make web on the
flower, bud, or leaves, suck sap, deform buds, and growth is stopped.
Control:
Spray Neem oil or use insecticides like Confidor or amidacloprid.
•Mites:
Red Spider mites attack in May/June in dry season.Make web below leaves, which can
be easily identified by theior crawling growth habit of brownish tiny insects.
Control:
Spray water underside the leaves every 45 days interval. Avoid miticides because they
have Sulphur, which burns the leaves in summer. In unavoidable, use Oberon.
•Termites:
White ants colonize in soil particularly in dry areas which inhabit the roots and lower
plant parts, which stop growing.
Control:
Apply Chlorophyriphos or Larsban @ 250 mL per 20 Liter or Kerosene oil can also be
used while irrigation.
•Scales:
These are round brown insects ,which stick on the stems/cane sand sucksap .Eventually
the stemdies
Roses are classified on several phenotypic bases, some common of which are as under:
1)On the basis of growthhabit:
o Groundcovers:
Roses with upto 1 feetheight.
o Miniatures:
Roses with 12 ft plant height.
o Dwarf Bushes:
Roses with less than 2 ft height.
o Bushes:
Roses with over 2 ft plant height, e.g., H.T. roses or floribundas.
o Standard roses:
Roses which are budded at a height of 3-3.5ft are called standard roses. These are
specialty roses, which are quite expansive but provide splendid floral displays onfocal
points in the landscape.
o Half standard: Roses which are budded at a height of 2-2.5ft are called half standard
roses.
o Weeping Standards: Roses which are budded at a height of 5 ft from ground level.
Usually weeping type of cultivars are budded in such type of roses.
o Climbers/ Ramblers: Roses with climbing nature, which need support along pillars.
2)On the basis of flower type:
Roses with less than 8 petals.
o Semi-doubles:
o Double flowers:
Roses with more than 20 petals. It is further divided intothree types:
o Moderately full:
Roses with 21-29 petals.
o Full double:
o Very full double:
Roses with more than 40petals.
3)On the basis of flowering habit:
o Floribunda
o Miniature
o Shrubs/bush roses
Types of roses:
1.Bush roses/ Old roses:
Rosa centifolia
Rosa chinensis Gruss-an-teplitz
Rosa bourboniana
Rosagallica
2.Modern roses:
Hybrid tea
Floribunda
Roses may also be classified on the basis of fragrance into no fragrant, slightly fragrant,
fragrant or very fragrant. Moreover, these may also be classified on the basis of flowering
period into Repeat flowering or once-flowering roses.
COMMERCIAL PROPAGATION:
•BushRoses:
They are propagated by hard or semi-hardwood cuttings. Best time of planting is from
November till end January when the plant is in dormantconditions.
•ModernRoses:
Rootstock through cutting, while scion cultivars are propagated through T-Budding in
July. In developed countries, stentling (grafting) is used.
Rootstocks for roses:
o Rosa Natal Briar(World)
o Rosa rugosa (World)
o Rosa canina (World)
o Rosa multiflora(World)



Comments
Post a Comment